Galvanized vs. Galvalume Steel Coils: Which Is Better for Roofing Projects?
Claim:
While both galvanized and galvalume steel coils are widely used for roofing, Galvalume generally provides longer service life and better performance in harsh or humid environments, whereas Galvanized steel remains a practical, budget-friendly choice for moderate climates and shorter-term projects.

Table of Contents
1. What Are Galvanized and Galvalume Steel Coils?
Both galvanized and galvalume steel coils start as carbon steel sheet that is coated to improve corrosion resistance. The coating is the key difference:
- Galvanized steel is coated primarily with zinc to provide sacrificial protection against corrosion.
- Galvalume steel is coated with an alloy of roughly 55% aluminum, 43% zinc, and 1–2% silicon — combining aluminum’s barrier protection and zinc’s active protection.
2. Key Differences in Composition and Performance
The two coatings perform differently under real-world conditions:
- Galvanized steel provides good protection in moderate, dry environments at lower cost.
- Galvalume offers superior corrosion resistance in high humidity, coastal or industrial zones due to its aluminum-zinc barrier effect.
- Galvalume reflects more sunlight and heat, helping roofs stay cooler and last longer.
- Galvanized may show visible white rust if moisture is trapped during storage or installation.
- Galvalume can last 40–70 years under typical roofing exposure; galvanized about 20–50 years depending on conditions.
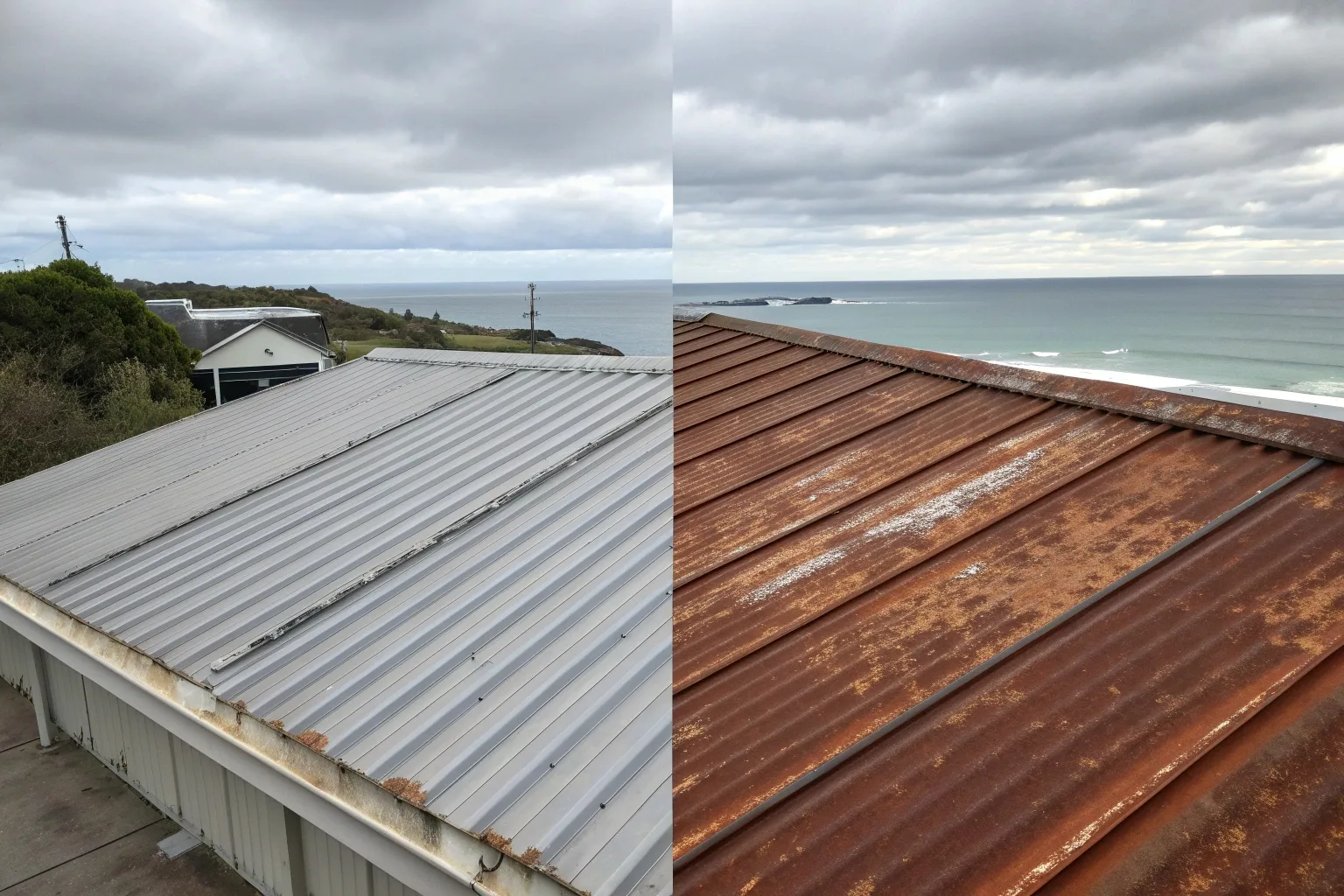

3. Advantages and Disadvantages for Roofing Applications
Each material brings its own balance of cost, performance and application suitability:
| Property | Galvanized Steel | Galvalume Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Coating Composition | ~100% Zinc | 55% Al / 43% Zn / 1–2% Si |
| Corrosion Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Heat Reflectivity | Medium | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Best Environment | Dry, Inland | Coastal, Humid, High UV |

4. How to Choose the Right Coil for Your Climate and Budget
Selection depends on the balance between environmental exposure and budget priorities:
- For coastal, industrial, or humid regions: Choose Galvalume for long service life and low maintenance.
- For moderate or dry inland climates: Galvanized may provide sufficient protection at lower cost.
- For agricultural or concrete-contact environments: Galvanized sometimes performs better chemically.
- For architectural or energy-efficient roofs: Galvalume’s high reflectivity helps reduce heat gain.

Conclusion
For most modern roofing applications, Galvalume steel coils deliver longer service life and better all-weather protection, especially in humid or coastal areas. However, Galvanized steel coils remain a solid, cost-effective option for dry climates or short-term structures. Understanding the environment, exposure and lifecycle cost will help you select the right material for your roofing projects.





