Why Aluzinc (GL) Coils Are Gaining Popularity in Construction and Roofing

In recent years, Aluzinc (GL) steel coils have become one of the most preferred materials for roofing, wall cladding, and industrial construction. Their growing popularity is not just a trend—it’s a reflection of real performance advantages over traditional galvanized steel.
This article explores why more global buyers, engineers, and project contractors are switching to Aluzinc, and what makes it the smarter long-term investment for modern construction.
Table of Contents
1. What Makes Aluzinc (GL) Steel Coils Different from Galvanized Coils
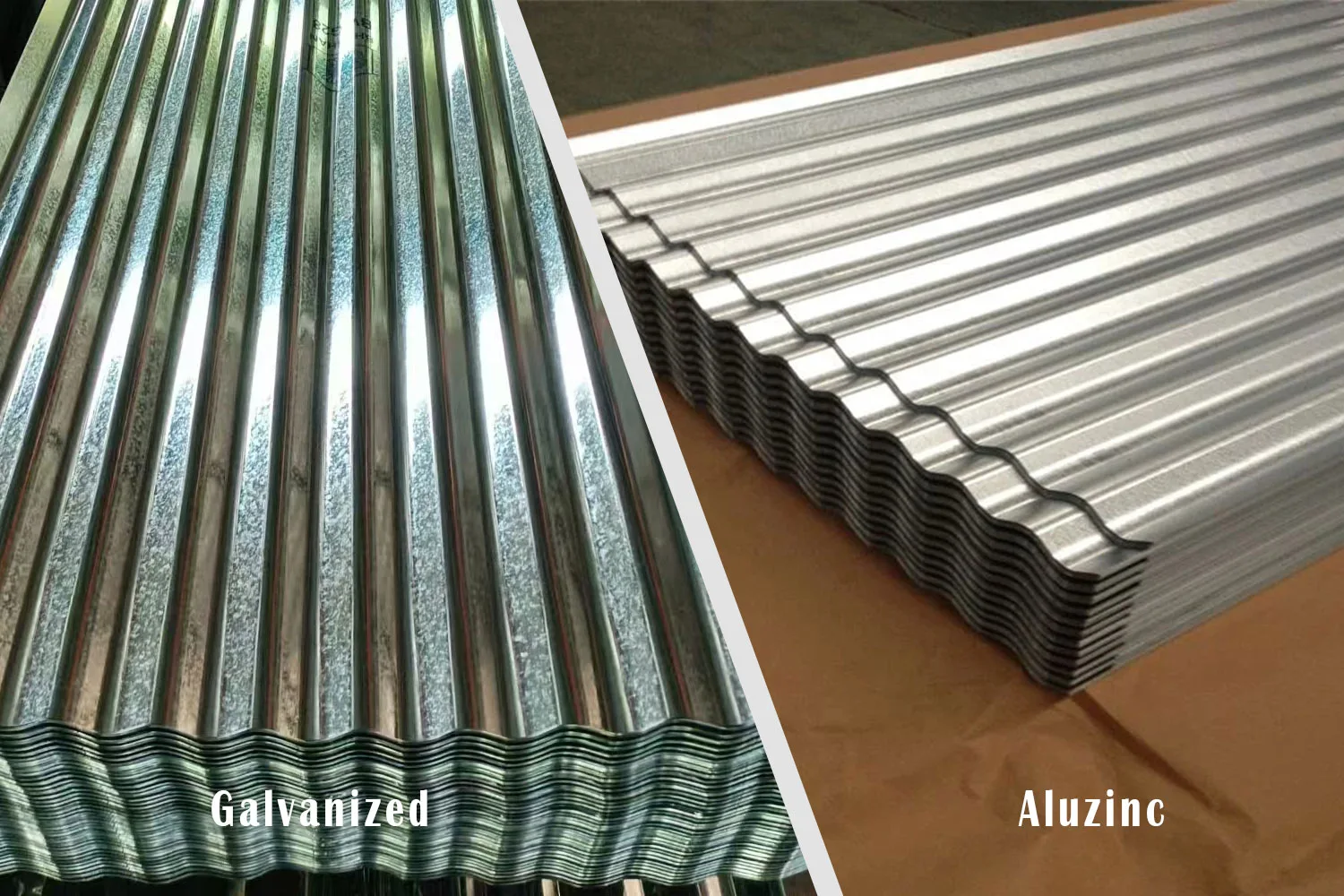
While galvanized steel is coated with pure zinc, Aluzinc (also known as GL or Galvalume) is coated with an alloy of approximately 55% aluminum, 43.4% zinc, and 1.6% silicon. This small change in chemistry delivers a major upgrade in performance.
The aluminum forms a tough barrier layer that prevents rust, while zinc provides galvanic protection. The result? Superior corrosion resistance, smoother surface finish, and longer lifespan—often two to six times that of regular galvanized steel.
In addition, Aluzinc coils offer a bright, reflective, and uniform metallic surface that’s ideal for roofing aesthetics or as a substrate for color coating (PPGL).
2. Advantages of Aluzinc Coatings in Harsh Environments
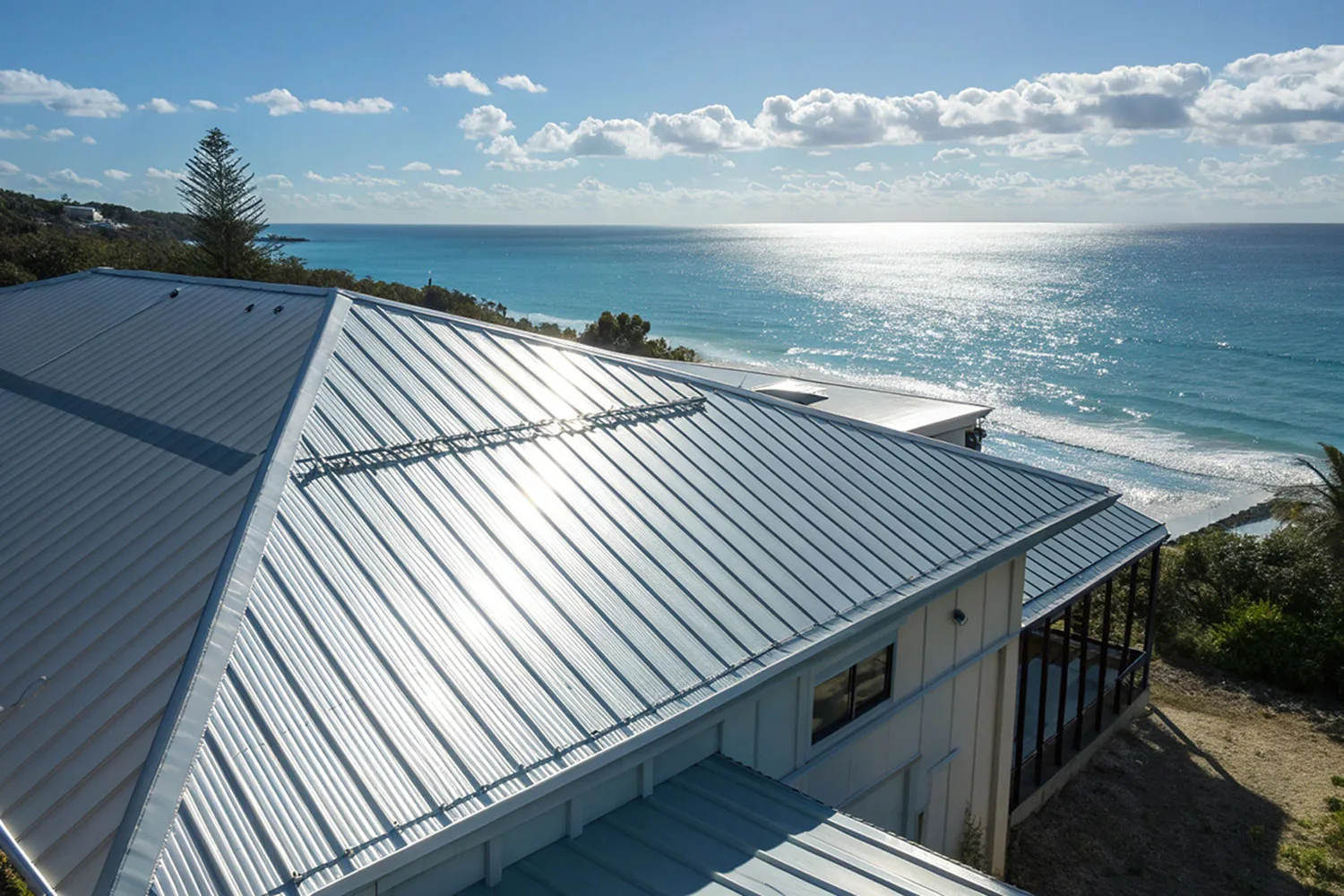

When exposed to marine or industrial atmospheres, Aluzinc coatings outperform galvanized coatings dramatically. The aluminum component prevents oxidation, while zinc continues to protect cut edges and scratches through galvanic action.
- Longer service life — up to 3–6 times that of galvanized steel.
- Better heat reflectivity — reduces roof temperature by up to 6°C, lowering energy costs.
- Excellent resistance to humidity and acid rain — perfect for coastal and high-moisture areas.
- Less white rust — improved storage and shipment performance.
This makes Aluzinc the go-to material for applications where both durability and aesthetic performance matter.
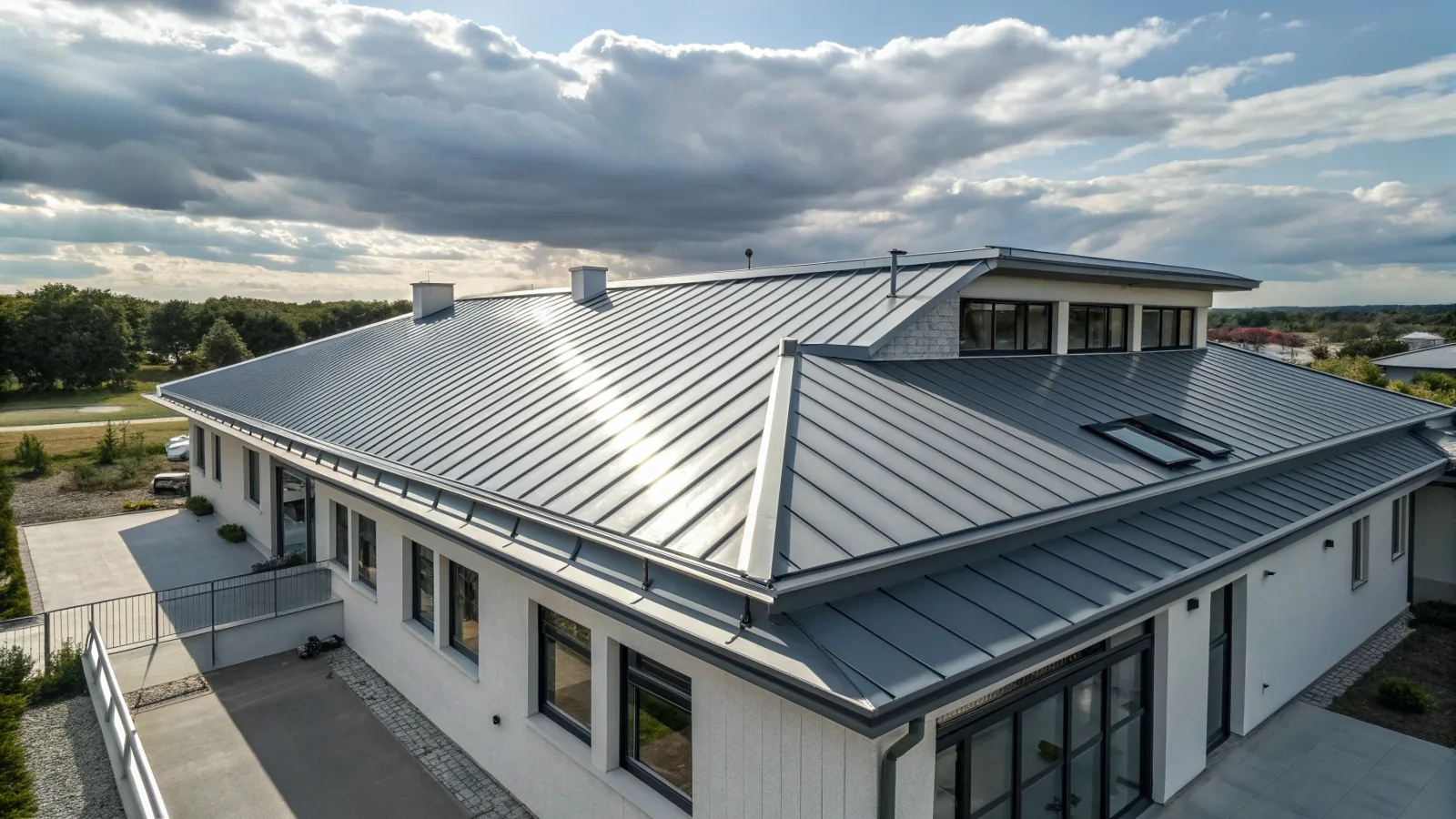
3. Applications in Modern Roofing and Structural Projects
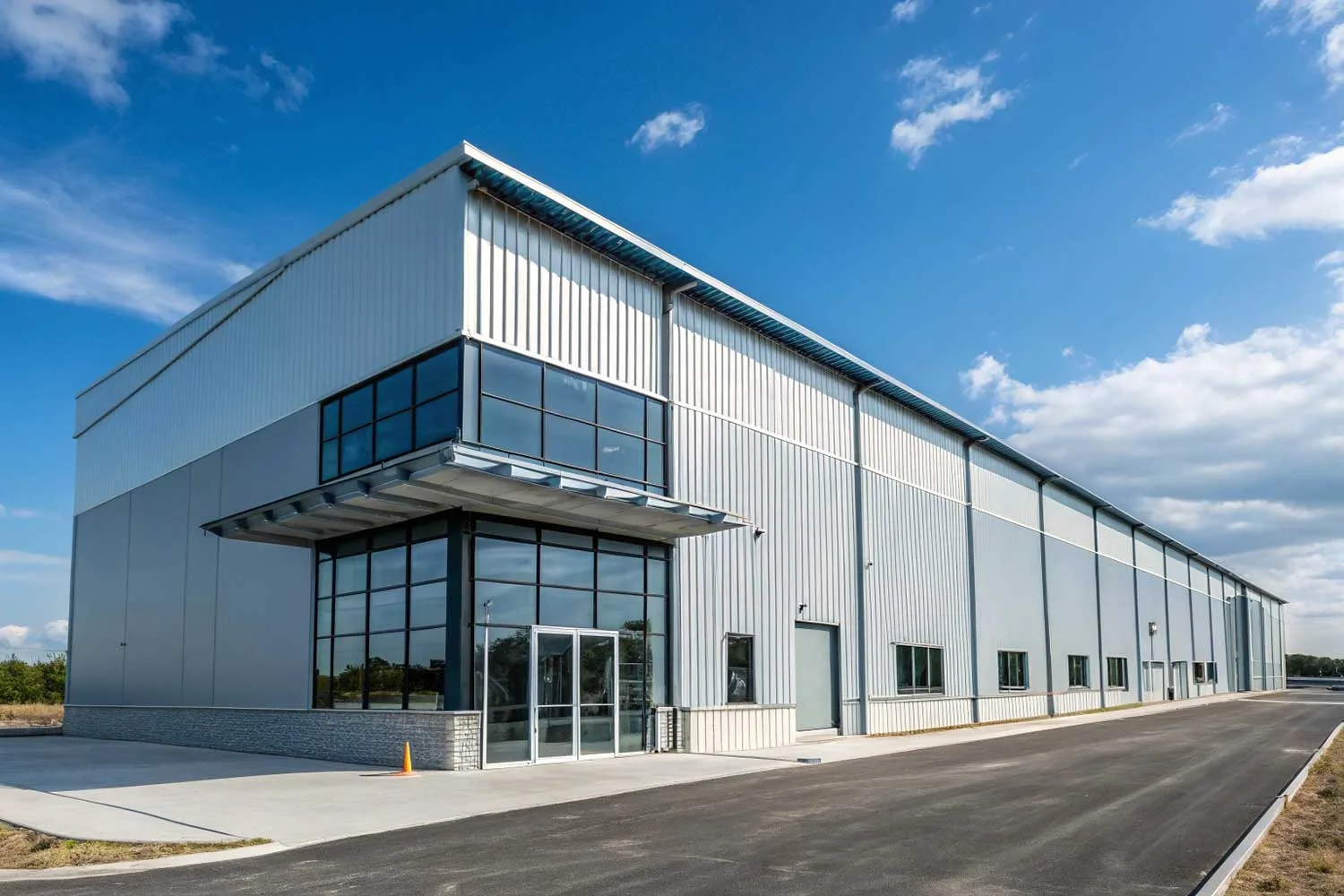

Today, Aluzinc coils are widely used across industrial buildings, warehouses, workshops, and residential roofing systems. Their superior corrosion resistance and reflective properties make them ideal for environments that demand performance and visual appeal.
Typical applications include:
- Corrugated and trapezoidal roofing sheets
- Sandwich panels and composite walls
- HVAC ducting, ceiling panels, and garage doors
- Solar panel bases and pre-painted color coating substrates
For long-span roofing systems or color-coated projects, Aluzinc’s smooth surface enhances coating adhesion and reduces maintenance costs over time.
4. Market Insights: Why Global Buyers Are Switching to GL Coils

According to recent market trends, demand for Aluzinc steel has surged due to several practical and economic reasons:
- Longer product lifecycle — buyers benefit from fewer replacements and lower maintenance costs.
- Better export value — many contractors and importers prefer GL over GI for high-end projects.
- Price stability — as Aluzinc offers better performance per dollar spent.
- Eco-friendly advantage — higher solar reflectivity contributes to energy-efficient buildings.
- Global specification alignment — GL complies with ASTM A792, EN 10346, and JIS G3321 standards.
Claim
“Aluzinc isn’t replacing galvanized steel — it’s redefining what durability and design can mean for modern construction.”
Final Thoughts
From factories to modern homes, Aluzinc (GL) coils are proving their value in both performance and appearance. For steel wholesalers and construction buyers, understanding the differences and benefits can help you make smarter purchasing decisions — and deliver roofs and structures that truly last.





